
To connect with a remote system, you’ll need an open and stable version of SsH.

Although it is commonly used for secure access and file transfers over local systems, SSH can also be used to create tunnels for other encrypted network applications.
#MANAGE SSH TUNNEL MAC MAC OS#
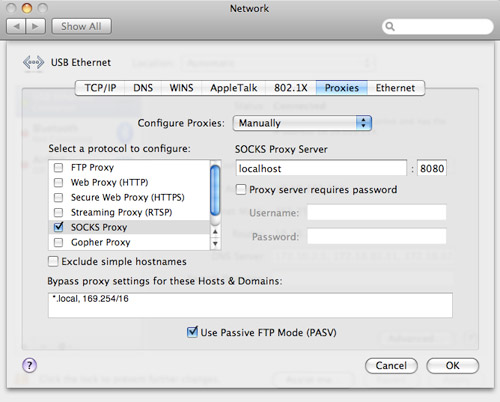
Tunnel management can be performed using the command line via Mac OS X’s built-inSSH client. What should I do to set up a SH tunnel on my MacBook pro? SSH is a method of connecting to servers that is supported by Mac OS. Your SSH tunnel is now up and running! To use it, simply connect to localhost:5901 with your VNC client. Once you’re logged in, leave the Terminal window open. Enter the following command, replacing “remote_host” with the IP address or hostname of the remote computer: ssh -L 5901:localhost:5901 _host 3. To set up an SSH tunnel on a Mac, you’ll need to have a few things: – A Mac OS computer – An SSH client (we recommend using the built-in Terminal app) – The IP address or hostname of the remote computer Once you have these things, follow the steps below to set up your SSH tunnel. SSH tunnels are also a good way to bypass firewalls that block certain types of traffic. Tunneling traffic through an SSH connection is a great way to securely connect to a remote computer, especially if you’re on a public Wi-Fi network. SSH tunnels are a way to securely connect to a remote computer by forwarding traffic through an encrypted tunnel. SSH, or secure shell, is a protocol that allows you to securely connect to a remote computer. This guide will walk you through the process of setting up an SSH tunnel on a Mac OS computer. If you’ve ever wanted to set up an SSH tunnel on a Mac, you’ve come to the right place.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
