
And so we have a 1.52 kilograms sample of our molecule in question, of glucose so if we can figure out the mass per mole, or another way to think about it, the molar mass of glucose, If I say a mole of something, I'm saying that's Avogadro's
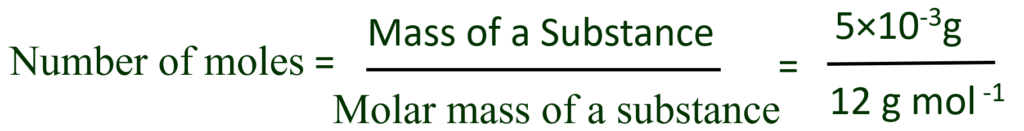
If I said a dozen of something, you'd say oh, that's 12 of that thing. Remember, mole is really, you can view it as a Trying to figure out the number of moles, So like always, pause this video and try to figure this out on your own and this periodic table ofĮlements will prove useful.

We are asked to calculate the number of moles in a 1.52 So the final answer should be reported as 180.16 g/mol. So the 5 digit get upgraded to a 6 in the answer. Since the number we're discarding (6) is larger than 4 we round the digit it is next to up one number. So we only want the 1 and 5 digits and want to discard the 6. But because we only have two decimals digits for the 72.06 and 96.00 numbers, our answer is limited to two decimal digits. So after multiplying Sal is performing this calculation: 72.06 + 84.156 + 96.00, which mathematically would yield 180.156. For addition the sig fig rule is that we can only have as many decimal digits as do in the calculation number with the lowest number of decimal digits. You should look into sig figs in greater detail, but in this problem Sal is adding three numbers together. And the rules we use to judge how many digits are permissible are significant figures, or sig figs. But in science we are more conservative with the digits we use because of the precision of our measuring instruments. After a calculation would be able to use all the digits of the final number as our answer if we only wanted a mathematical answer. One important application is `stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture´ ( SILAC).It's important to keep in mind significant figures are important for doing calculations in a science like chemistry. In addition, 13C is used to quantitate proteins (quantitative proteomics). Such compounds are safe because they are non-radioactive. In the following formula the result should be rounded to the nearest integer:Ĭ = number of C atoms X = amplitude of the M ion peak Y = amplitude of the M+1 ion peakġ3C-enriched compounds are used in the research of metabolic processes by means of mass spectroscopy. In the above the mathematics and chemistry have been simplified, however it can be used effectively to give the number of carbon atoms for small to medium sized organic molecules.

Similarly a molecule containing two carbon atoms will be expected to have an M+1 peak of approximately 2.2% of the size of the M peak, as there is double the previous likelihood that a molecule will contain a 13C atom. A molecule containing one carbon atom will be expected to have an M+1 peak of approximately 1.1% of the size of the M peak as 1.1% of the carbon atoms will be 13C rather than 12C. This is known as the M+1 peak and originates due to the presence of 13C atoms. In this way proteins with a 13C content of almost 100% can be produced.Ī mass spectrogram of an organic compound will usually contain a small peak of one mass unit greater than the apparent molecular ion peak (M). This is achieved by growing microorganisms genetically engineered to express the protein on a growth medium with 13C labeled glucose as the only carbon source. In biological NMR proteins can be deliberately labelled with 13C (and usually nitrogen-15) to facilitate structure determination. Acquiring a 13C NMR spectrum can take from a couple of minutes to hours because many scans have to be summed together in order to have results distinguishable from background noise. Since 12C has zero spin, it does not give an NMR signal, and since only 1% of the atoms in a molecule are 13C, it is unlikely that carbon-carbon coupling is seen.
This is a technique that gives information on the identity and number of atoms adjacent to other atoms in said molecule, thereby giving clues to the structure of an organic molecule. The absorption and emission of the RF signal by the nuclei can be monitored and detected using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy. Because of its nuclear spin properties, this isotope responds to a resonant radio frequency (RF) signal.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
